Some information about the battery.
Lithium Energy Japan will produce LI-ION batteries for PHEV. The cathode consists of Lithium-Manganese Dioxide with polyvinylidene Fluoride as a binder and graphite for conductivity.<
/p>In the 90s, the demand for a lightweight rechargeable cell to fuel the fast-rising market for portable electronic equipment drove the development of lithium-ion batteries. Beginning with cameras and mobile phones, the technology has evolved into the preferred power source for everything from cordless power tools to large-scale energy storage and automotive applications.
The Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV battery consists of 80 Lithium Ion cells arranged in 10 modules. Total voltage when fully charged 328 Volts when discharged 288 Volts. 80 cells of 3.7 volts make a battery pack of 296 volts, but commercially we talk about a 300-volt battery, the cells are all in series. The cells are grouped in 10 modules of 8 cells, so 10 modules make the total battery pack, some model years possibly different cell numbers and types.
The battery pack for the Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV does not contain the same LEV50N cells as the one for the i-MiEV. Instead, LEV40 cells are used. Particularly for PHEVs, these cells were created. For use in electric vehicles, GS Yuasa also provides cells other than LEV50N. They already have LEV75 cells, which increase capacity by 50%. The LEV50N’s energy density, which is only 110 Wh/kg, is the lowest of all current electric vehicles. The energy density would increase to 165 Wh/kg if the LEV75 cells weigh the same. Not that difficult considering how much more energy-dense most modern cells are. The new LEV75 cells may therefore be lighter than previously thought.
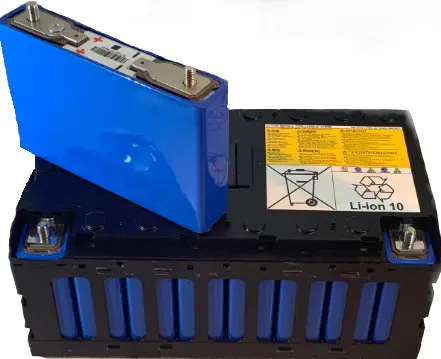
YUASA LEV40 Cell
Nominal voltage 3.65V
Operating voltage range 2.65V to 4.0V
1-hr rate typical Capacity 25oC 40Ah
Length 170 (±1)mm
Width 35 (±1)mm
Height (over terminals) 100 (±1)mm
Mass 1.65Kg
Charge – 1C (50Amp) Constant current followed by 4.1V constant voltage charge. 5500 cycles to 80% of the initial capacity.
Lithium-ion battery vs lead acid battery
- Consistent capacity and high-rate discharge
- Quick Charging
Lithium-ion Battery – Charges in one hour
More than 9 hours on a lead acid battery - Compact footprint and low floor loading
- High energy throughput and cycle life
Lithium-ion battery with a capacity of 50Ah and a throughput of 25000Ah
Lead acid battery with a capacity of 100Ah and a throughput of 5000Ah - Extremely high energy efficiency
4% heat loss with 96% output from a lithium-ion battery
Lead acid battery with a heat loss of 15% and an output of 85% - State of Charge Partial Excellence
- Power Protection
Lithium-ion Battery – Battery Management Systems detect and notify faults.
There is no information available on lead-acid batteries. - Wide temperature range for charging – no voltage compensation
- Thermal management at a lower cost
Air circulation is permissible with a lithium-ion battery.
Air cooling is essential for lead-acid batteries. - No gas emissions
- Lead Acid Battery – Hydrogen ventilation required Lithium-ion Battery – Operates in a sealed container
- Non-toxic with no restrictions on recycling
Lithium-ion Why?
The most crucial elements that make lithium-ion cells essential in mobile phones and electric vehicles alike are their high energy density and numerous discharge cycles. They outperform conventional battery chemistries in a variety of different ways, though. In addition to having a greater energy density, the cells can discharge at higher power and recharge much more quickly. Operating lithium-ion batteries constantly at a partial state of charge is not detrimental in situations where charging power or time may be constrained, such as solar PV systems or stop-start vehicles. Compared to lead-acid cells, they have more operating flexibility as a result.
Lithium-ion batteries barely interact with the outside world. Since charging cells are inefficient, there are no gas emissions and very little heat is lost during the charging process. This indicates that lithium-ion batteries can be used in closed cabinets that are totally separated from their environment. The cells should be recycled at the end of their useful lives, but they don’t contain any harmful substances under control like cadmium, mercury, or lead.
Battery management is crucial for the secure operation of lithium-ion multi-cell batteries. Battery management’s major job is to charge all of the cells in a battery to the same level and keep them there for the duration of the battery’s lifespan. By keeping an eye on the voltages of each individual cell within a battery, battery management accomplishes this. To bring the pack’s voltages into line, higher voltage cells are discharged.
When compared to conventional battery technology, Battery Management’s extensive data collection makes it possible to precisely monitor the battery condition and provides increased security. Additionally, this improved intelligence lowers maintenance costs and increases battery life.
Some information for dbcam is here: Mitsubishi Outlander PHEV DBCAM OR RESET
What happens with used cells?
Lithium batteries have a high risk of fire and explosion and produce a lot of energy. Because of this, it takes specialised engineers to dispose of and disassemble these batteries. The Lithium Battery Recycling Solutions business employs engineers with specialised training in handling the high-voltage components found in lithium-ion batteries, and it operates out of a cutting-edge workshop. The demand for safe and dependable lithium battery disposal is increasing along with the use of electric power in vehicles and other equipment. However, this is not a simple task.
Another solution for the reuse of the old cells for households is for a qualified person to compare and pair the cells and build the system to store the power with the solar system but for that, no any figures on how much the cost is and what is the saving on that.


0 Comments